
What Is Two Shot Injection Molding and When Is It Used? - double injection moldi
Author:gly Date: 2024-10-15
Blow molding is a type of plastic forming process for creating hollow plastic products made from thermoplastic materials. The process involves heating and inflating a plastic tube known as a parison or preform. The parison is placed between two dies that contain the desired shape of the product...
After a specified time, the mold is transferred from the heating chamber to the cooling chamber. Here, the molten resin cools and solidifies before the finished plastic product is removed from the mold. Rotationally molded products are known for their exceptional quality, durability, and strength.
Rubber injection molding is when uncured rubber is transformed into a usable product by injecting raw rubber material into a mold cavity made of metal. The applied pressure produces a chemical reaction like...
In the United States and Canada, there are many machines available for rotational molding. These machines play a crucial role in modern manufacturing, allowing for the cost-effective and efficient production of a wide range of plastic products. This capability supports industries such as automotive, furniture, medical devices, and toys. Below, we discuss several leading machines used in rotational molding.
Urethane casting is the process of injecting polyurethane and additive resins into a soft mold usually made of silicone elastomer. The casting process is similar to injection molding; injection molding differs by using hard, metal molds...
When selecting a polymer for rotational molding, it's important to consider the specific requirements of the process, which can limit the choice of thermoplastics in the following ways:
A grommet edging is a flexible rubber or plastic strip that covers rough and sharp surfaces found in openings and edges of panel walls to protect the passing electrical cables, wires, and other sensitive components...
Features: The Caccia BI-AX model is a bi-axial rotational molding machine that enables the production of double-walled and multi-layered plastic parts. This capability enhances structural integrity and offers versatile design possibilities for various applications.
Rock and Roll Machine: Rock and roll machines feature molds contained in cradles that swing back and forth at a 45-degree angle on a horizontal axis while simultaneously rotating 360 degrees on a perpendicular axis. This dual-motion process is ideal for producing long parts with small diameters, such as canoes and kayaks.
Whether you’re creating a functional prototype or a visual prototype, hire an expert to assist you throughout the way.Top-rated plastic prototype manufacturers ensure the right type of prototyping to ensure success. At Global Technology Ventures, you can create a precision prototype using the highest-quality material. Our experts can mimic the appearance and operation of any production part. To refine your design with one of the best prototype companies today, get in touch with our experts this instant!
Clamshell Machine: Clamshell machines are single-station units where both molding and cooling take place within the same chamber. The mold, along with the resin, is loaded and unloaded through the front panel. During the heating and molding process, the front panel and cover are locked. Once molding is complete, the cover is opened to facilitate cooling, and the mold swings out of the open oven.
Features: The RL-3200 Carousel Machine is renowned for its large production capacity and flexibility. It is capable of producing large, complex parts with excellent control over the molding process. Additionally, its user-friendly interface simplifies operation and management.
In the 1940s, rotational molding was employed to create doll heads and other small toys using polyvinyl chloride plastisol resin and electroformed nickel-copper molds. The setup included electric motors and gas burners, with the finished parts being quenched in cold water. This method attracted various industries, leading to the production of road cones, marine buoys, and armrests.
Rotational molding is used in a wide range of applications, including industrial and automotive parts, furniture, materials handling equipment, medical devices, toys, and more. Some of the notable products created through rotational molding include:
Plastic caps and plugs are two distinct ways for sealing the ends, tops, and openings of tubes and containers. Caps are placed over the opening, and plugs are placed in the opening. Due to the many varieties of...
Rotational molding is a non-pressure molding process, which reduces the cost of mold toolings as they do not need to withstand high pressure. This process allows for the creation of a wide range of sizes, from small to very large, and can produce complex plastic shapes. Additionally, there are minimal design restrictions, offering designers the flexibility to incorporate intricate details into their products.
The commonly used polymers in rotational molding are presented below. Most of these polymers are thermoplastics, which can be easily reshaped by heating.
Polyethylene grades used in rotational molding include High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), Medium-Density Polyethylene (MDPE), and Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE).
The system operates with continuous mold cycles, eliminating downtime between operations. Plastic is injected into the first mold, which then moves to the cooling station. Meanwhile, a second mold is positioned for clamping and plastic injection. As the second mold cools, the first mold begins the injection process again. This alternating sequence allows for efficient production without waiting for each mold to cool before starting a new cycle.
Features: The CARROUSEL ROTO series by Rotomachinery Group features independent arm controls, making it well-suited for producing a diverse range of plastic products with varying shapes and sizes. These machines offer customizable molds and efficient heating systems.
Many of the products used daily are made possible by producers and suppliers of rubber and plastic. These substances are robust, adaptable, and capable of practically any shape required for various industrial purposes. Several varieties are...
Finally, the process still requires manual steps, such as demolding, due to the limited automation options available. This necessity for manual intervention increases the overall operational costs.
Shuttle Machine: Shuttle machines feature independent arms that rotate biaxially, transporting the mold through combined stations for loading, cooling, and unloading, while moving to a central heating chamber on the track. Once the molding process is complete, the mold returns to its original position. These machines are advantageous for maximizing floor space, as their design allows for efficient use of the manufacturing area while maintaining a streamlined workflow.
The standard setup for a rotational molding operation includes an arm or cradle that holds the mold, along with one or more ovens and cooling chambers. The main difference among various machines lies in the direction the mold travels, which follows the sequence of the rotational molding process. The types of machines used in rotational molding include:
The molds used in the shuttle process are designed similarly to standard molds but must be engineered to fit the specific dimensions and requirements of the shuttle molding process. The tooling remains standard, with minimal modifications needed to accommodate the conditions of shuttle molding.
Polyurethane rollers are cylindrical rollers covered by a layer of elastomer material called polyurethane. Depending on the application, the inner roller core is prone to scratches, dents, corrosion, and other types of damage...
A polyurethane bushing is a friction reducing component that is placed between moving and stationary components as a replacement for lubricants. The use of polyurethane for the production of bushings is due to...
Heating: The powdered resin is heated inside the hollow mold while being rotated slowly until it melts. As the resin melts, it evenly coats the entire inner wall of the mold. The combination of heating and slow rotation ensures uniform distribution of the resin. The mold typically rotates biaxially at a speed of less than 15 RPM.
Today, rotational molding is utilized for producing larger and more complex parts, thanks to a better understanding of the process and significant advancements in equipment design. Despite these improvements, long heating and cooling cycles still pose a challenge for some manufacturers. Ongoing development efforts are focused on modifying rotational molding equipment to meet the increasing demand.
Demolding or unloading: The cooled part is carefully removed from the hollow mold. An air ejection system can assist in lifting the part out of the tool. Once removed, the part moves on to subsequent processes, such as inspection and packaging.
Vertical Wheel Machine: Vertical wheel machines function similarly to a Ferris wheel. The molds are held in cradles and move through the loading, heating, cooling, and unloading stages as the wheel rotates. The loading and unloading stations are situated at the bottom of the wheel, positioned between the heating and cooling areas. Vertical wheel machines are suitable for molding small to medium-sized parts.
Inexpensive tooling: Rotational molding molds do not need to withstand high pressures, allowing them to be manufactured from cost-effective materials like aluminum. This reduces the investment required for tooling, especially beneficial for short production runs.
Plastic coating is the application of liquid polymers or plastic on the surface of a workpiece by dipping or immersion. The result is a thick plastic finish for protective and decorative purposes. This gives the material additional resistance against...
The concept of rotational molding is straightforward, but achieving high-quality results can be challenging for some manufacturers. Despite its complexities, rotational molding is highly valued for its advantages over other molding methods. With proper design and settings, both manufacturers and end-users can benefit from the following:
Turret or Carousel Machine: Turret machines revolve around a central pivot and feature three to six arms, each with a mold attached. These molds pass through various stations in sequence loading, heating, cooling, and unloading as the carousel rotates. These recirculating machines use an MMI interface combined with a programmable logic controller (PLC) for operation.
Rotational molding, often known as "rotomolding," is a plastic casting technique used to create large, hollow parts that are seamless and frequently double-walled. The process involves three main stages: First, a specially designed mold is placed on a rotating frame. Second, the mold is heated in a chamber while rotating, allowing the plastic material to melt and evenly coat the interior. Finally, the mold is transferred to a cooling chamber where it continues to rotate, solidifying the plastic into the final shape. This technique is valued for its ability to produce durable, large-scale components with smooth, seamless finishes and can accommodate both single and double-wall designs.
The cooling time of the polymer is as crucial as the heating time. Therefore, determining the proper cooling rate is essential. Rapid cooling can lead to uncontrollable warpage and shrinkage of the part, while slow cooling can cause uneven flow of the molten resin, resulting in inconsistent wall thickness.
Thank you for your interest in Global Technology Ventures. To know more about our Products, request a quote or ask a question,
To ensure even wall thickness distribution, the correct rotation ratio must be determined. This ratio is the number of rotations per minute (RPM) on the horizontal axis divided by the RPM on the vertical axis. For spherical or cubic molds, a rotation ratio of 4:1 is typically used. For irregularly shaped solids, the ratio may need to be adjusted to 1:8 or 8:1, depending on how the manufacturer optimizes the process.
Silicone rubber molding is a method for shaping, forming, and fabricating silicone rubber parts and products using a heated mold. The process involves compressing or injecting silicone rubber into a mold...
The shuttle method was developed to address the inefficiencies associated with mold cooling time, which can lead to diminishing returns. By utilizing the cooling phase productively, the process maximizes efficiency. In addition to time savings, shuttle molding machines also offer significant cost advantages.
Thermoplastic molding is a manufacturing process that works to create fully functional parts by injecting plastic resin into a pre-made mold. Thermoplastic polymers are more widely used than thermosetting...
Some swing arm mold machines are equipped with two arms at each corner of the oven, resulting in a configuration of four arms with two pivot points. These machines are capable of continuous operation, eliminating the need for stoppages for maintenance or mold changes.
Polyurethane molding is the process of fabricating or manufacturing plastic parts by introducing a urethane polymer system into a tool or mold and allowing it to cure. Like any other type of plastic, the excellent processability...

Plastic injection molding, or commonly referred to as injection molding, is a manufacturing process used in the mass fabrication of plastic parts. It involves an injection of molten plastic material into the mold where it cools and...
Fiberglass molding is a method for forming complex and intricate parts using fiberglass resin. Though there are several reasons for producing parts and components from fiberglass, the most pressing reasons are the...
Marine vehicles and equipment for transportation and water sports such as rowing boats, canoes, buoys, and kayaks produced in a rock and roll molding machine
This article presents all the information you need to know about rotational molding. Read further and learn more about the following:
Cooling: During this stage, the molten polymer inside the mold hardens and solidifies into the desired shape. The moldâs exterior is cooled by natural or forced convection, typically with air. To ensure dimensional stability during cooling, air may also be supplied internally to the mold. Water sprays can be used to accelerate cooling, but this may impact the partâs mechanical properties and dimensions.
A mold release agent is a coating applied to the inner walls of the mold to facilitate the easy removal of the molded part after cooling and to prevent sticking to the mold surface. The types of mold release agents include:
Raw materials for rotomolding vary based on their physical properties and intended applications. Additives and colors are incorporated to achieve the desired characteristics. The primary materials used in rotomolding are polyethylene types, which are thermoplastics that can be reshaped through heating. The five types of polyethylene used are linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), medium-density polyethylene (MDPE), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE).
The arms of a carousel rotational molding machine are motorized and operate independently of the central hub, oven temperature, or dwell time. The turret rotates 120 degrees at the end of each cycle and progresses to the next position, ensuring that all arms remain active and never idle. This design facilitates continuous operation and efficient workflow, though it may require more complex controls and maintenance compared to simpler systems. Additionally, the independent arm configuration allows for greater flexibility in molding various sizes and thicknesses, but it may come with higher initial costs and operational demands.
Polyethylene: Polyethylene makes up more than 80% of the polymers used in rotational molding due to its low cost and ease of processing. Available in powdered form, it simplifies the molding process compared to other polymers that are more challenging to grind. Polyethylene also offers good chemical resistance and low water absorption.
Primary additives enhance the mechanical properties of the molded part and facilitate the molding process. Flow modifiers improve the flow of the polymer resin when molten, ensuring even thickness distribution. Heat stabilizers prevent thermal degradation from high temperatures. Fillers increase the stiffness of the part, while impact modifiers boost impact strength; however, their use must be controlled to avoid rough surfaces and reduced flow. Secondary additives provide additional characteristics to the finished product, such as colorants, flame retardants, and anti-static agents.
High Cycle Times and Costs: Rotational molding can be less suitable for high-volume production due to its lengthy cycle times. The process involves slow rotation during heating to melt the material and a gradual cooling phase for both the part and the mold, which extends the overall molding cycle. While cooling systems like water or air can help, they add to the overall cost.
The origins of rotational molding can be traced back to ancient Egypt, where ceramics were produced using early molding techniques. The more advanced application of rotational molding emerged in 1855 with the production of artillery shells and in 1910 when the Swiss used the technique to create hollow chocolate eggs with uniform wall thickness and density. During these periods, several patents were registered to document the process, but it was considered slow and faced challenges, preventing it from gaining widespread popularity.
Swing Machine: Swing machines feature independent arms, allowing for selective operation of some arms to enhance production efficiency. Mounted at the corners of the oven, these arms rotate biaxially, swinging the mold between the heating and cooling chambers. With a capacity of up to four arms, swing machines are ideal for materials that require extended cooling and demolding times compared to heating.
Molding is a manufacturing process that uses a mold - the latter being a solid container used to give shape to a piece of material. It is a forming process. The form is transferred from the mold to the material by...
Ease of Decoration: Designers can effortlessly add textures and symbols to the surface of the tooling, allowing for seamless incorporation of decorative elements.
Plastic overmolding has a long and interesting history, dating back to the early 1900s. The first overmolding process was developed by German chemist Leo Baekeland, who invented Bakelite, the first synthetic plastic. Baekeland used a...
Rock and roll machines feature two arms, each performing a 360-degree rotation in one direction. While spinning, the arms rock back and forth to evenly distribute the plastic within the mold. To boost productivity, the molds are preheated before being loaded into the machine.
Pulverized Resin: Pulverizing or milling transforms pellets or coarse powders into fine or extra-fine powder. The particle sizes vary depending on the machine, so the plastic material may need to pass through several pulverizers to achieve the desired consistency. Methods of pulverization include batch pulverization, dry milling or grinding, and wet pulverization. The choice of method depends on the specific requirements of the molding process for which the pulverized plastic will be used.
Plastic bottles are bottles made of high or low-density plastic, such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC), or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Each of the materials mentioned has...
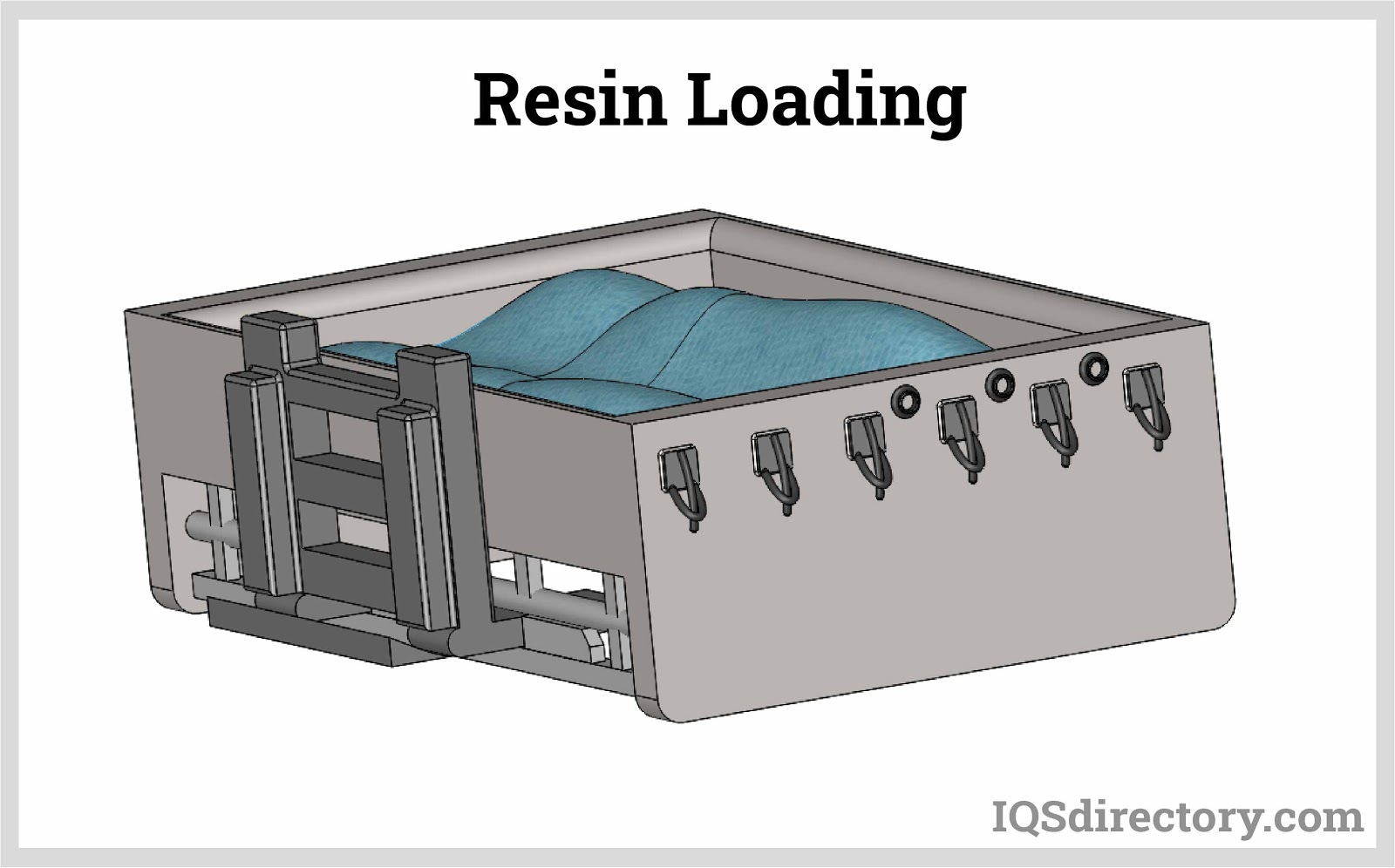
Loading: A measured quantity of polymer in powdered resin form is placed into a hollow mold and securely closed. The resin powder should be finely sized, homogeneous, and dried to ensure good flow and to prevent bubble formation. The amount of resin loaded into the mold plays a crucial role in determining the wall thickness of the finished part.
Please note that the rotational molding machine market is dynamic, and newer models may have emerged since this update. Therefore, it's advisable to conduct further research to ensure you have the latest and most accurate information.
As rotational molding offers many advantages over other types of molding processes, it does not mean that it is the best for all manufacturers. Here are some disadvantages of this process:
Rubber molding is a process of transforming uncured rubber or an elastomer into a usable product by transferring, compressing, or injecting raw rubber material into a metal mold cavity...
Once you have gathered this information, the prototyping specialist can help you make an informed choice of the best type of plastic and manufacturing approach to take for your prototype. The typical plastics used in prototyping have specific properties that dictate the best application of each material.
Rotomolding primarily uses polyethylene resin as its raw material, which is introduced into the mold to start the process. During heating, the mold is rotated within the chamber. The moldâs frame is designed to ensure rotation around every point of its axis. As the mold turns, the resin evenly coats the interior surface, resulting in a finished product with consistent and uniform thickness throughout.
Urethane wheels are wheels made of molded urethane, also known as polyurethane. Urethane is an elastomer that comprises urethane carbamate linkages and is a portmanteau phrase for elastic polymer...
The hollow mold, typically made from cast aluminum or fabricated steel sheet, imparts the desired shape to the molded part.
The heating time of the polymer is crucial in determining the quality of the finished part. Excessive heating can lead to thermal degradation of the polymer, reducing its mechanical properties such as wear and impact resistance. Conversely, insufficient heating can result in incomplete melting of the polymer. Unmelted grains will not properly blend with the molten resin, leading to bubble formation and adversely affecting the product's mechanical properties.
Picking the right material for a plastic product prototype can be a challenging task. The material options vary in strength, appearance, and durability. Choosing an appropriate material requires expert knowledge. A plastic prototype service will offer solutions based on your project requirements. They can even help you test different plastic products to find your optimal material.
Material handling equipment, such as durable crates, stackable pallets, containers, and insulating boxes, which are uniquely produced through rotational molding
Carousel rotational molding machines can feature between three and six arms, each positioned at different stages of the process. They are available in fixed and independent arm designs. Independent arm models can accommodate more arms that move separately, allowing for the use of additional molds and molds of varying sizes, heating, and thicknesses.
There are several methods to perform rubber overmolding, and each method has its own unique advantages and disadvantages. The choice of method typically depends on the design and material requirements of the product being...
Features: The ARM PR-8 is a versatile rotational molding machine featuring multiple arms, which provides precise and efficient molding. It comes with advanced controls and energy-efficient heating systems, ensuring consistent production of high-quality plastic parts.
Features: The ROTO2000 by Persico is a rotational molding machine renowned for its ability to produce seamless, hollow products such as tanks and containers. It is celebrated for its reliability and consistent performance in large-scale production.
Fiberglass is a plastic reinforced material where glass fiber is used as reinforcement, and the glass fiber is flattened into a sheet. It is also known as glass fiber reinforced plastic or glass reinforced plastic...
Secondary Processes: These may include painting, coating, assembly, welding, and the addition of inserts, among others. The specific secondary processes applied depend on the intended use and requirements of the finished product.
Rotational molding produces a variety of products, including kayaks, sports helmets, display mannequins, water storage tanks, baby cribs, and road construction barriers. This method efficiently and cost-effectively creates large plastic items, offering both versatility and affordability in manufacturing.
GETTING A QUOTE WITH LK-MOULD IS FREE AND SIMPLE.
FIND MORE OF OUR SERVICES:


Plastic Molding

Rapid Prototyping

Pressure Die Casting

Parts Assembly



